You may determine roughly how many dissolved minerals are in your water supply by using a water hardness calculator. Calcium (Ca2+) and magnesium (Mg2+) are two minerals that may be found in your tap water. While they may be suitable for your health in some ways, they may also cause problems like scaling in your pipes, boilers, and heaters, which can lead to clogs and decreased performance. Keep reading to learn how to determine the water’s hardness.

While there are some minor health benefits to drinking hard water, there are fundamental problems it presents in mechanical settings, where water hardness must be monitored to prevent the deterioration of boilers, cooling towers, and other water-handling equipment. Local indicators of hard water include the absence of suds when detergent is stirred into the water and the formation of limescale in kitchenware and plumbing fixtures. Hard water is an issue all around the world, and water softeners are commonly employed to mitigate the adverse effects of hard water.
This is why knowing the hardness of your water supply is essential. The hardness of your water supply can be determined and optimizations made to assist your machinery last longer. It’s also important to check the water hardness to see whether it can save you money on repairs or the replacement of expensive machinery used in manufacturing or processing. Check the water hardness, temporary hardness, and permanent hardness levels.
Table of Contents
What is Water Hardness?
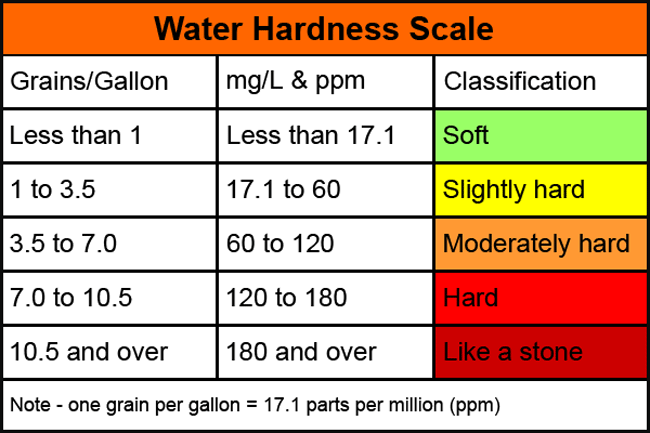
What makes your water hard is the number of minerals like calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide that are in it. Mineral content varies widely between soft and hard water.
| Image | Product | Details | Coupon Code | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
SALT-BASED WATER SOFTENER Springwell Water Whole House |
Type: Ion Exchange Grain Capacity: 32,000 – 80,000 grains Flow Rate: 11 – 20 GPM Warranty: Lifetime |
MHWT5 | Check Price |
 |
SALT-FREE WATER SOFTENER Kind Water Systems Whole House |
Type: Template Assisted Crystallization Grain Capacity: N/A Flow Rate: 15 GPM Warranty: Lifetime |
MHWT5 | Check Price |
The use of hard water in the home can lead to several undesirable outcomes, such as the development of limescale in pipes and appliances, the appearance of filmy residue on the skin, the appearance of white spots on glassware, and the decrease in the efficiency of certain appliances.
How can you calculate the hardness of water using a water hardness calculator?
Steps to determine water hardness are as follows:
- Put in the calcium concentration in millimoles per liter.
- Simply type in the mg/L concentration of magnesium that you have measured.
- The water hardness calculator will now provide results in milligrams per milliliter of calcium carbonate.
Example of using the water hardness calculator
To determine how much calcium and magnesium are in the water supply in milligrams per liter (mg/L) Calcium concentration is 31 mg/L, and magnesium concentration is 27 mg/L.
Calculate the inverse of the reciprocal of the water’s hardness.
- Put in 31 mg/L for the calcium concentration value.
- Specify a magnesium concentration of 27 mg/L.
For the water hardness calculator:
- Hardness Formula = Calcium * 2.497 + Magnesium * 4.118
- Hardness = 31 * 2.497 + 27 * 4.118 = 188.6
- The water hardness value is 188.6 mg/CaCo3L. According to the hardness scale, this water is very hard.
| CaCo3 concentration (mg/L) | Water hardness indication |
| 0 to 60 | Soft water |
| 60 to 120 | Moderate hard water |
| 120-180 | Hard water |
| Greater than 180 | Very hard water |
Units For Measuring the Total Hardness in Water
Water hardness is measured in various units like:
- Grains per gallon (GPG)
- Parts per million (PPM)
- Milligrams (of calcium) per liter (mg/L)
- Dgh or dH (usually used for the hardness of the water in fish tanks)
The GPG scale is the standard for measuring water hardness. Total hardness can also be measured in parts per million or milligrams per liter. Dissolved mineral concentrations of 20 parts per million (PPM) are equivalent to 20 milligrams per liter (mg/L).
Temporary Vs Permanent Hardness
There is a distinction between temporary and permanent hardness. The main distinctions between the two are discussed below.
Temporary Hardness
Calcium hydrogencarbonate (Ca (HCO3)2) and magnesium hydrogencarbonate (Mg (HCO3)2) in solution in water produce a temporary hardness. This is because both of these minerals are soluble in boiling water. Lime softening, in which lime (calcium hydroxide) is added to temporarily reduce a substance’s hardness, is another option.
Permanent Hardness
The magnesium and calcium chlorides and sulfates in permanent hardness are the main ingredients. When calcium chloride, magnesium chloride, or sulfate is present in the water, it is considered permanently hard. Calcium hardness and magnesium hardness both contribute to what is known as “permanent hardness.” Permanent hardness can only be remedied with specialized equipment, such as an ion exchange water softener because these minerals are not destroyed by boiling.
How Can I Test Water Hardness at My Home?
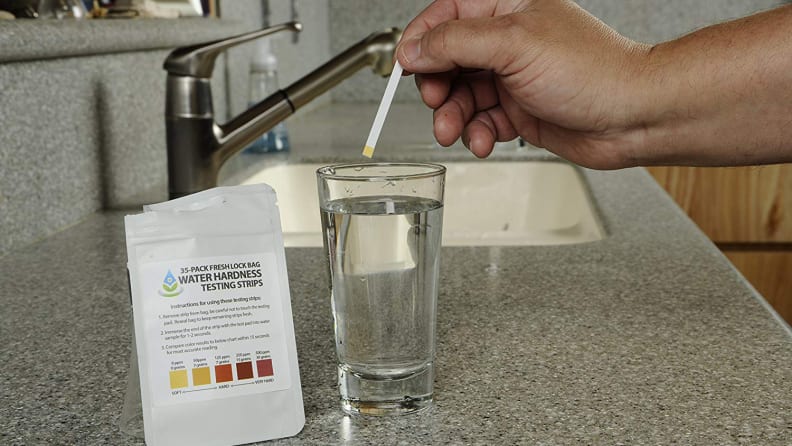

A home water hardness test can be conducted in several methods, including with a store-bought kit, in a lab, or even with a bar of soap.
How Can You Calculate Water Hardness With Test Strips
Step 1. Choose Your Water Source
Look for an outdoor faucet to determine the hardness of the water coming into your site if you want to know how it was before it was treated. A source that hasn’t been filtered or distilled can also be tested.
To avoid any potential interference with your readings, you should not draw water from a garden pipe. Water gathered from an external source can be verified by allowing it to flow until the level stabilizes.
The hardness of Processed Water: Look for a water supply that originates from the water softener or whole-house water filler to determine the efficacy of your water softener.
Take the test strip out of the container. Make sure the detecting pad doesn’t come into contact with your skin, as this could skew the results.
Step 2. Insert The Test Strip

Put the water sample and the test strip into the clean glass. Sit for 2 seconds, or as directed by the kit’s manufacturer. Do not soak the test strip in water for more than a few minutes, as this could lead to false readings.
Extrude the strip and give it a good shake to get rid of the surplus moisture. It’s important to keep waving until all the water has evaporated. In general, you want to make sure there’s a very subtle hint of moisture on the piece.
Keep the strip vertical for a minimum of 10 seconds and a maximum of 30 seconds. The artwork may show chemical reaction indicators within this time frame.
Step 3. Read The Water Hardness
If you want to know how hard your water is, check the color of the test pad on your strip against the water hardness chart on the box. Typically, the kind of water testing kit you use will determine the colors you see.
Your treated water should have a hardness measurement of 0 if it is being used correctly. A higher range, up to 425, is normal for untreated water.
Testing With a Laboratory
For the most accurate reading of hardness in either treated or untreated water, a laboratory test is a way to go.
Typically, lab testing includes:
- Test tubes with labels
- Packing for dispatch
Your water’s magnesium and calcium carbonate hardness will be determined once you collect samples and return them to the lab. This type of test will provide you with the precise hardness of your water in PPM, mg/L, or GPG.
Using the Soap Test
One of the least reliable methods for determining the hardness of water is the soap test. The results will not be specific, but they will indicate whether or not you have hard water. A soap test can tell you about the chemistry of your water because soap reacts differently depending on whether it is soft or hard.
What you’ll need for this testing is:
- A water bottle that is transparent
- Refreshing water straight from the tap
- Soap for the dishwashing
About three-quarters full is ideal; add a few drops of dish soap and shake. First, give the bottle a good shake, and then examine the water within. It’s challenging if the water is milky white and there is no visible layer of bubbles on the surface. The water is gentle if it is transparent and has a thin layer of bubbles on the surface.
Analyzing Your Results
Your water hardness test results can help you determine if a water treatment system is necessary for your home.
Soft to moderately hard water has a hardness measurement of 0 to 5 GPG, or less than 60 PPM or mg/L. Having a water softener is probably unnecessary if your water has a hardness of less than 5 GPG (or 60 PPM or mg/L).
Hardness readings between 180 parts per million (ppm) or mg/L (milligrams per liter) categorize water as moderately hard to very hard. Water softening treatment is recommended for these levels of hardness to reduce the risk of harm to your home.
Treating Your Hard Water
A water softener is the most effective solution for dealing with hard water. Moreover, Ion exchange is the process by which water softeners swap out the calcium and magnesium ions in your water for sodium ions. Put in at the point where the main water line enters the house, they protect the entire house from the effects of mineral deposits in the water.
When it comes to mitigating the negative impacts of hard water, water conditioners are a close second. Water conditioners, on the other hand, do not remove minerals or lower the total hardness; instead, they merely crystallize the already present hardness minerals, rendering them incapable of forming scale.
Frequently Asked Questions

Is 200 PPM considered hard water?
Yes. There is a clear indication that your water is hard if the hardness reading is over 180 parts per million (PPM), and a reading of 220 PPM indicates extremely hard water.
What is the typical water hardness?
Water does not have a typical hardness. The geology of your area and the methods used to treat the public water supply will affect the hardness of your tap water.
Conclusion:

Minerals are dissolved in water. But when there are a lot of them, the water is tough. Magnesium and calcium are examples of such elements. The following items may be required to remedy the aforementioned issues:
- Calcite or lime for softening water
- This can be determined with the use of a bottle of soap.
- Invest in a cheap water testing kit if you want reliable results.